Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Nanofabrication facility, Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215123, China
3 Research Center of Laser Crystal, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
4 Hangzhou Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Hangzhou 311421, China
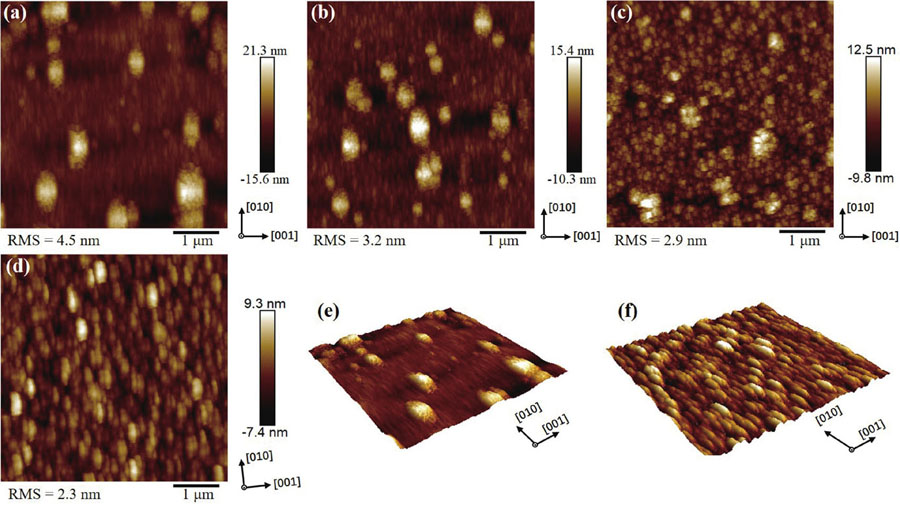
Homoepitaxial growth of Si-doped β-Ga2O3 films on semi-insulating (100) β-Ga2O3 substrates by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) is studied in this work. By appropriately optimizing the growth conditions, an increasing diffusion length of Ga adatoms is realized, suppressing 3D island growth patterns prevalent in (100) β-Ga2O3 films and optimizing the surface morphology with [010] oriented stripe features. The slightly Si-doped β-Ga2O3 film shows smooth and flat surface morphology with a root-mean-square roughness of 1.3 nm. Rocking curves of the (400) diffraction peak also demonstrate the high crystal quality of the Si-doped films. According to the capacitance–voltage characteristics, the effective net doping concentrations of the films are 5.41 × 1015 – 1.74 × 1020 cm−3. Hall measurements demonstrate a high electron mobility value of 51 cm2/(V·s), corresponding to a carrier concentration of 7.19 × 1018 cm−3 and a high activation efficiency of up to 61.5%. Transmission line model (TLM) measurement shows excellent Ohmic contacts and a low specific contact resistance of 1.29 × 10-4 Ω·cm2 for the Si-doped film, which is comparable to the Si-implanted film with a concentration of 5.0 × 1019 cm−3, confirming the effective Si doing in the MOCVD epitaxy.
homoepitaxial growth MOCVD Si-doping films high activation efficiency Ohmic contacts Journal of Semiconductors
2023, 44(6): 062801

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Hangzhou Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Hangzhou 311421, China
Sb-doped crystals were grown using the optical floating zone (OFZ) method. X-ray diffraction data and X-ray rocking curves were obtained, and the results revealed that the Sb-doped single crystals were of high quality. Raman spectra revealed that Sb substituted Ga mainly in the octahedral lattice. The carrier concentration of the Sb-doped single crystals increased from to , the electronic mobility depicted a decreasing trend from to , and the electrical resistivity varied from 0.603 to 0.017 ·cm with the increasing Sb doping concentration. The un-doped and Sb-doped crystals exhibited good light transmittance in the visible region; however, the evident decrease in the infrared region was caused by increase in the carrier concentration. The Sb-doped single crystals had high transmittance in the UV region as well, and the cutoff edge appeared at 258 nm.
Sb-doped β-Ga2O3 crystal growth optical properties electrical properties Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(4): 041605
1 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心,绵阳 621900
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所,上海 201800
2022年12月13日,美国能源部(DOE)及其下属的国家核安全管理局(NNSA)宣布,劳伦斯利弗莫尔国家实验室(LLNL)利用其建立的国家“点火”装置(NIF),在人类历史上首次实现了聚变产能大于驱动聚变发生的激光能量这一“点火”里程碑,将为美国核**物理规律和效应研究、核**库存管理等提供重要支撑,为未来清洁能源的发展铺平新的道路,并为高能量密度物理研究提供新的手段和平台。本文专访了中国工程物理研究院激光聚变研究中心郑万国研究员,就发布会传递信息、惯性约束聚变(ICF)实现途径及存在难点、激光聚变“点火”历程、未来ICF和惯性聚变能(IFE)发展前景,以及激光晶体在ICF和IFE中重要作用等业界广泛关心的几个问题进行解读,以期为读者提供专业的信息,使大家进一步了解ICF发展趋势和IFE发展前景,并针对相关晶体材料开展基础研究及关键技术攻关,牵引和支撑未来激光聚变驱动装置建设。
聚变“点火” 国家“点火”装置 可控核聚变 惯性约束聚变 聚变能 激光晶体 非线性晶体 fusion “ignition” national ignition facility controlled nuclear fusion inertial confinement fusion fusion energy laser crystal nonlinear crystal
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Four single crystals (Yb0.15Lu0.85xY0.85-0.85x)3Al5O12 (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1) were grown by the Czochralski method. The correlation of the host atom Lu:Y ratios with the density and the luminescence properties were revealed. The density increases linearly with increasing of content, which will improve the gamma ray cut-off ability. The integrated intensity of the X-ray excited luminescence spectrum increases exponentially with the increasing Y:Lu ratio, while the decay time becomes even shorter with the increasing content. These results will provide a basis to balance the comprehensive properties to match different application requirements.
Yb:LuYAG scintillators Czochralski method charge transfer Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(12): 121601
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
利用提拉法生长了Si4+共掺杂Yb∶YAG单晶, 该晶体属于立方晶系, Oh10-Ia3d空间群。掺杂的Si4+没有改变YAG的晶体结构, 但是影响了发光离子的价态。吸收光谱表明Si4+的引入使得Yb2+含量增多, 这是由于Si4+引入了过量的电荷, 为满足电价平衡, Yb3+转换为Yb2+。Yb2+的出现降低了Yb∶YAG的发光强度。稳态X射线激发发射光谱结果表明Si4+共掺杂Yb∶YAG晶体的发光强度是Yb∶YAG的63%, γ射线激发下的光产额降至原来的40%。此外, 由于原料中含有多种Yb的同位素, Yb∶YAG除了可以被X射线、γ射线激发出荧光外, 还可以与中子发生核反应产生带电粒子, 进而引起次级反应产生荧光。荧光的产生仍然由Yb3+决定, 因此, Si4+掺入也降低了中子探测灵敏度。
Si4+掺杂 Yb∶YAG晶体 提拉法 闪烁性能 探测灵敏度 Si4+ doping Yb∶YAG crystal Czochralski method scintillation property detecting sensitivity
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光材料重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
β-Ga2O3 作为宽禁带半导体材料, 以其优越的光学性质、电学性质和广阔的应用前景近年来受到国内外学者的广泛关注。基于本研究团队在如何制备 β-Ga2O3 单晶及如何通过掺杂五族离子实现对 β-Ga2O3 单晶电学性质及光学性质的调控两个重要课题上的深入研究, 对 β-Ga2O3 单晶的制备方法、Ta5+ 与 Nb5+ 掺杂 β-Ga2O3 单晶的电学性质及光学性质进行了综述。
材料 β-Ga2O3 单晶 制备方法 光学性质 电学性质 material β-Ga2O3 single crystal preparation method optical properties electrical properties
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料与光电研究中心, 北京 100049
概述了本课题组在KDP类晶体快速生长领域的研究及进展情况。通过集成生长设备的管道系统、升级连续过滤系统、研发晶体生长过程的实时监控系统以及高精度退火设备, 实现晶体生长系统的集成化; 通过数值模拟优化晶体表面流场状态、全流程量化控制实现晶体稳定生长以及精密热退火进一步提升晶体性能; 针对点籽晶快速生长KDP类晶体中存在的柱锥交界面问题, 相继提出了长籽晶锥区限制生长法和长籽晶自由生长法, 为大尺寸高性能KDP类晶体生长提供新的技术方案。
KDP类晶体 快速生长 集成化 工艺优化 长籽晶 KDP-type crystal rapidly grown integration process optimization long-seed
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所薄膜光学实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料与光电研究中心, 北京 100049
3 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强激光材料重点实验室, 上海 201800
采用反应电子束蒸发技术在不同氧分压下制备了HfO2薄膜,并采用X射线衍射仪、扫描电子显微镜、椭圆偏振仪、X射线光电子能谱仪、1064 nm弱吸收测试仪、1064 nm激光1-on-1损伤测试系统等,对HfO2薄膜的结构、光学性能、化学组分、吸收性能、抗激光损伤特性和损伤形貌等进行了表征和分析。当沉积温度为200 ℃时,所制备的HfO2薄膜为单斜多晶结构,晶粒尺寸约为10 nm。随着氧分压升高,薄膜的氧化程度随之增大,由化学计量比缺陷主导的薄膜1064 nm弱吸收系数变小,同时薄膜结构变得疏松,折射率随之降低。深入研究后发现,在采用反应电子束蒸发技术制备HfO2薄膜时,提高氧分压有助于抑制膜内纳米吸收缺陷和基底亚表面裂纹,提高HfO2薄膜抗1064 nm激光损伤阈值,对制备出基于HfO2薄膜的高性能光学元器件具有重要的参考价值。
薄膜 反应蒸发 氧分压 抗激光损伤特性

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing100049, China
3 School of Aerospace Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing100084, China
4 Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing100084, China
To reduce the seed length while maintaining the advantages of the cuboid KDP-type crystal, a long-seed KDP crystal with size $471~\text{mm}\times 480~\text{mm}\times 400~\text{mm}$ is rapidly grown. With almost the same high cutting efficiency to obtain third harmonic generation oriented samples, this long-seed KDP-type crystal can be grown with a shorter seed than that of the cuboid KDP-type crystal. The full width at half maximum of the high-resolution X-ray diffraction of the (200) crystalline face is 28.8 arc seconds, indicating that the long-seed KDP crystal has good crystalline quality. In the wavelength range of 377–1022 nm, the transmittance of the long-seed KDP crystal is higher than 90%. The fluence for the 50% probability of laser-induced damage (LID) is $18.5~\text{J}/\text{cm}^{2}$ (3 ns, 355 nm). Several test points survive when the laser fluence exceeds $30~\text{J}/\text{cm}^{2}$ (3 ns, 355 nm), indicating the good LID performance of the long-seed KDP crystal. At present, the growth of a long-seed DKDP crystal is under way.
KDP crystal long-seed rapid growth High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2020, 8(1): 010000e6
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Sohag University, 82524, Sohag, Egypt
The rapid development of bulk β-Ga2O3 crystals has attracted much attention to their use as ultra-wide bandgap materials for next-generation power devices owing to its large bandgap (~ 4.9 eV) and large breakdown electric field of about 8 MV/cm. Low cost and high quality of large β-Ga2O3 single-crystal substrates can be attained by melting growth techniques widely used in the industry. In this paper, we first present an overview of the properties of β-Ga2O3 crystals in bulk form. We then describe the various methods for producing bulk β-Ga2O3 crystals and their applications. Finally, we will present a future perspective of the research in the area in the area of single crystal growth.
Journal of Semiconductors
2019, 40(1): 011801





